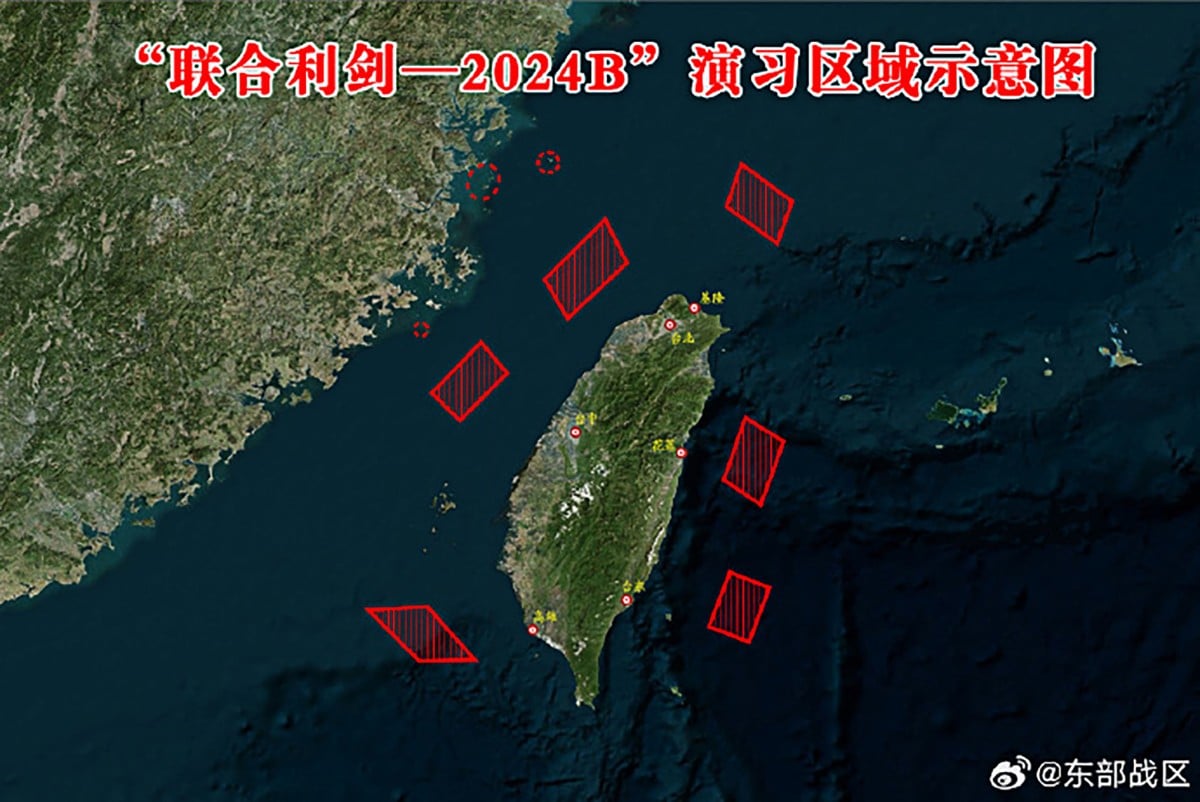
This handout from China’s People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Eastern Theatre Command released on October 14, 2024 shows a map of locations of the “Joint Sword-2024B” military drills being conducted by China around Taiwan. Agence France-Presse
BEIJING — China launched fighter jets and other aircraft over the Taiwan Strait on Monday as part of military drills aimed at sending a “warning” to the self-ruled island.
Here, AFP looks at the critical waterway and growing military flashpoint:
Where is the Taiwan Strait?
The strait separates the southeastern Chinese province of Fujian from the main island of Taiwan, home to around 23 million people.
At its narrowest point, just 130 kilometers (about 80 miles) of windswept water separates the two major landmasses, and several outlying Taiwanese islands — including Kinmen and Matsu — lie just a few kilometers from the Chinese coastline.
READ: Taiwan Strait — a history of crises
China and Taiwan have been governed separately since Mao Zedong’s communist army won a civil war and sent the opposition nationalist forces fleeing across the strait in 1949.
Why is it important?
The strait is a critical artery for global shipping through which a huge volume of trade passes every day.
Around $2.45 trillion of goods — more than a fifth of global maritime trade — transited the strait in 2022, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a Washington-based think tank.
READ: Taiwan says Chinese man detained after possible ‘intrusion’
Taiwan plays an outsized role in the global economy thanks to producing over 90 percent of the world’s most advanced computing chips, used in everything from smartphones to cutting-edge military equipment.
Analysts say a Chinese invasion would deal a catastrophic blow to these supply chains.
More minor disruptions, such as a blockade of the island, would cause costly shipping cancellations and diversions that would impact worldwide consumers.
“In the event of a long conflict over Taiwan, financial markets would tank, trade would shrivel, and supply chains would freeze, plunging the global economy into a tailspin,” Robert A. Manning, a China expert at Washington’s Stimson Center, wrote this year.
A report by the Rhodium Group estimated that a blockade of the island could cost firms dependent on Taiwan’s chips $1.6 trillion in revenue annually.
An invasion would also endanger Taiwan’s way of life, embodied by its democratic freedoms and boisterous elections.
It would also risk a wider conflict because the United States, while not recognising Taiwan diplomatically, has an agreement to help the island defend itself.
What has China announced?
Beijing said that it had launched military exercises called “Joint Sword-2024B” in areas to the north, south and east of Taiwan.
The armed forces deployed fighter jets, bombers and warships in the strait, and also simulated a rocket strike, state media said.
The military also said it had deployed an aircraft carrier, the Liaoning, to “strike on maritime and ground targets in the waters and airspace to the east” of the island.
The coast guard said four fleets were conducting “inspections” around the Taiwanese mainland and disclosed other patrols near Matsu.
The drills “test the joint operations capabilities of the theater command’s troops” while sending a “stern warning to the separatist acts of ‘Taiwan Independence’ forces”, according to Chinese authorities.
Taiwan has condemned the actions as “irrational and provocative”, and the US has called them “unwarranted”.
Has this happened before?
In late May, three days after the inauguration of President Lai Ching-te, China launched Joint Sword-2024A, an apparent precursor to the latest drills.
The Chinese military also held three days of drills encircling Taiwan in April last year in response to Lai’s predecessor, Tsai Ing-wen, meeting with then US Speaker Kevin McCarthy.
And in 2022, Beijing launched over a week of maneuvers after McCarthy’s predecessor, Nancy Pelosi, visited Taiwan.
Several major crises punctuated the preceding decades, most recently in 1995-6, when China conducted missile tests around Taiwan.
It is not yet clear how the drills announced on Monday compare in scale and intensity to those of previous years.

